New & Noteworthy
This page lists the enhancements and new features brought by Roboconf 0.5.
Target Definitions through the Web Console
It is now possible to define target.properties independently of any application.
This can be achieved through the web console.
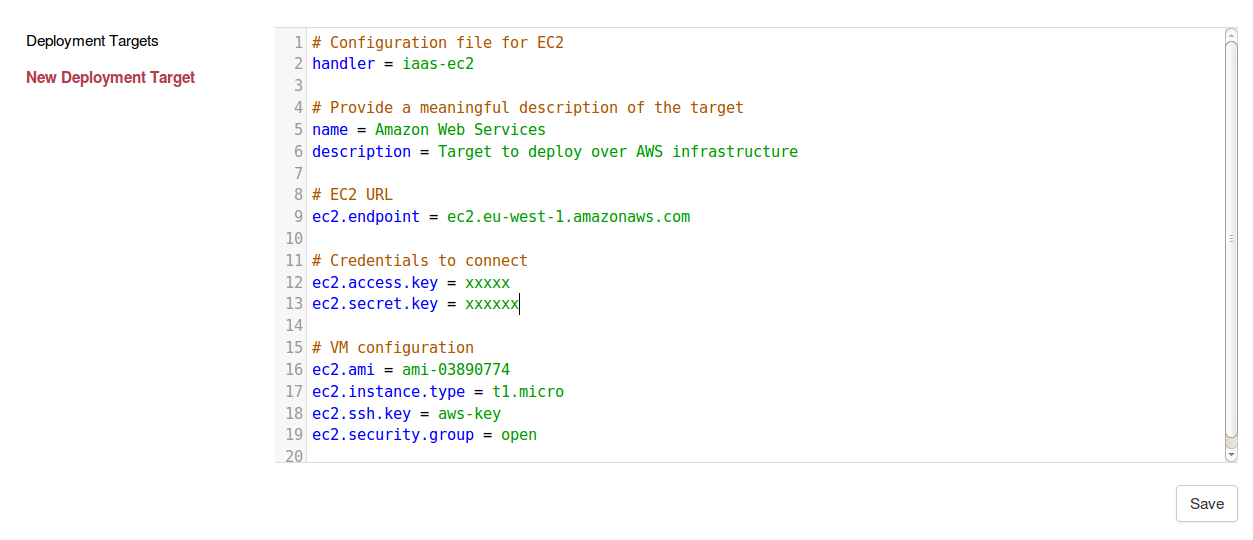
Pre-defined target.properties still work but are not mandatory anymore.
Deployment targets can then be associated with applications and application instances.

Combined with application templates, it allows to deploy a same application over different environments.
External Dependencies
Users can now define inter-application dependencies.
It means graph components from an application can reference variables exported by other Roboconf applications.
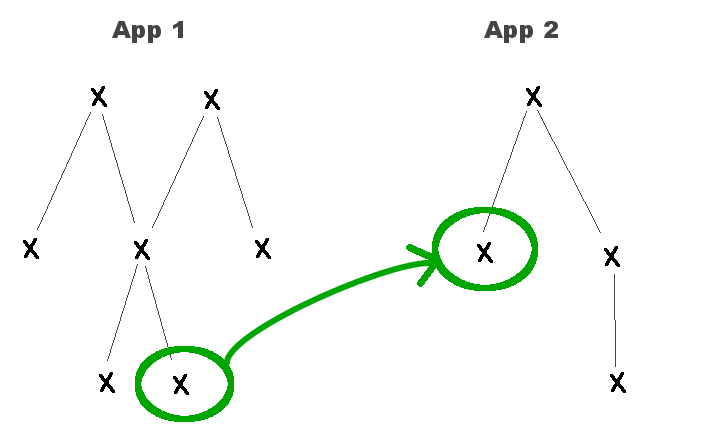
This is possible provided the other application marked some of its internal variables as visible from the outside.
# A global and unique export prefix
exports-prefix: Lamp
# Now, lets export the internal variable outside.
exports: Apache.ip as lb_ip
It can then be imported as…
MyApp {
installer: script;
imports: Tomcat.portAJP, Tomcat.ip; # local variables
imports: external Lamp.lb_ip; # external variables
exports: ip;
}
Inter-application links bind two applications together.
Application bindings are one-to-one relations.
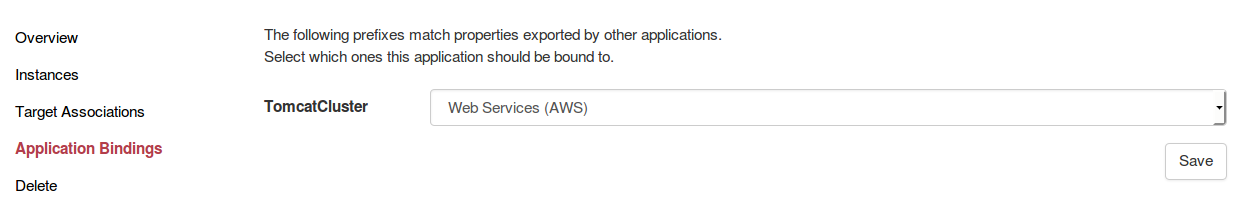
When a component from an application changes, and that this component exports variables to other applications, then these last ones
will be notified about it. This brings better modularity in applications management and provides a better approach when considering an information system.
Smarter Autonomic
The autonomic management has been completed to not execute silly reactions every time an agent probe triggers an event. Now, the autonomic manager verifies any previous automatic reaction has completed successfully before executing it again. It is also possible to define a safety delay between reaction executions.
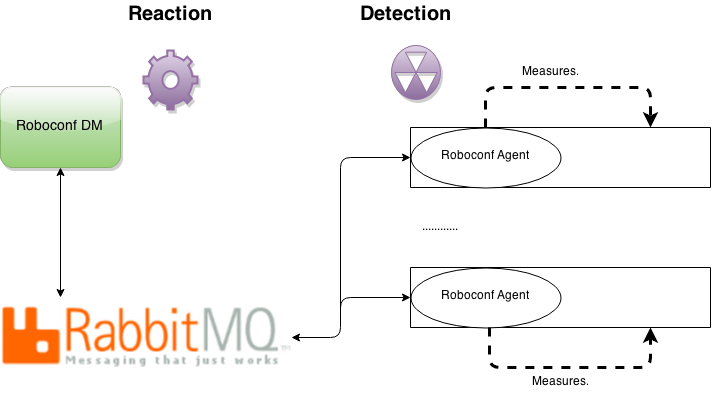
Eventually, we started to introduce the notion of quota.
For the moment, we only have a global quota that prevents the autonomic from creating too many virtual machines.
Other levels of quotas will be added in the next versions (per application, per infrastructure, etc).
Extensible Probe Framework
Since Roboconf 0.5, it is possible to create its own probe to measure activity on remote agents.
It means you can plug any Java-compliant library to monitor deployed software. Additional extensions
will complete the file, nagios and rest probes that come by default.
Such probes aim at being used with the autonomic management.
As an example, this feature was used to plug a JMX-based library in Roboconf to monitor Petals ESB.

Simplified Docker Configuration
The configuration to use the Roboconf Docker target has been simplified.
It provides the same features than before but with less properties.
As an example, the following configuration will automatically generate a Docker image, install and configure a Roboconf agent, start containers and install Software components (as defined in a Roboconf application).
# Common information to any target
handler = docker
name = Docker
description = A Docker installation with an image generated by Roboconf.
# Docker specific properties
docker.generate.image = true
docker.image = roboconf-docker-img
Miscellaneous
A lot of enhancements have been brought to this new version.
And many bugs were fixed too. Please, refer to the release notes for details.